Building craft is the mastery of construction skills combined with artistic vision, resulting in structures that are both functional and beautiful. It's defined by precision, material knowledge, and dedication to quality over speed—transforming raw materials into enduring works through hands-on expertise and problem-solving.
Why Building Craft Elevates Construction Beyond Basic Assembly
When you search for "craftsman: building craft," you're likely seeking more than dictionary definitions. You want to understand how true craftsmanship transforms ordinary construction into meaningful work. In today's world of rushed developments and disposable buildings, building craft represents a counter-movement where skill, patience, and respect for materials create spaces that last generations.
Unlike standard construction focused solely on efficiency, building craft integrates three non-negotiable elements:
The Building Craft Trinity
- Material Intelligence: Understanding how wood grain, stone density, or metal fatigue affects structural integrity
- Process Precision: Measuring twice, cutting once with tolerances under 1/16 inch
- Contextual Sensitivity: Designing solutions that honor both site constraints and human needs
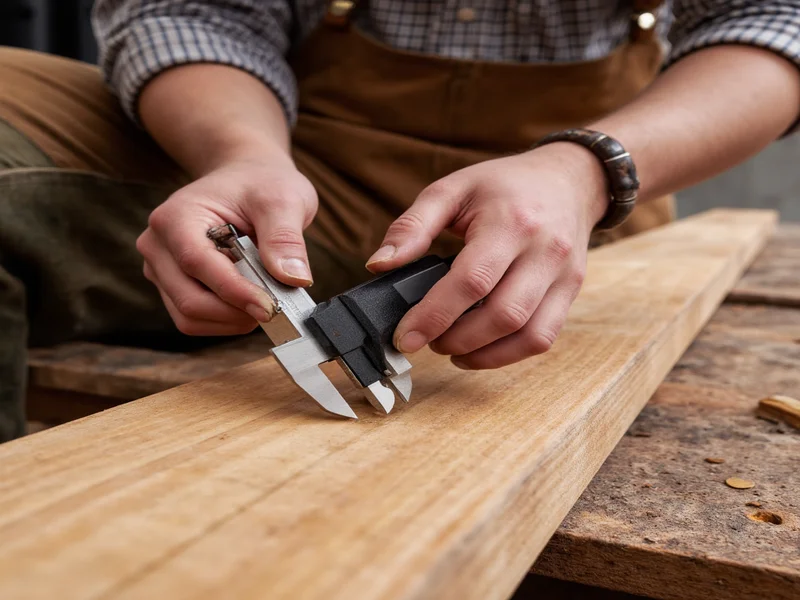

How Building Craft Solves Modern Construction Challenges
Mass production has eroded foundational skills, but building craft offers tangible solutions to contemporary problems:
| Industry Problem | Building Craft Solution | Real-World Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 30% material waste in standard builds | Adaptive reuse of imperfect materials | 40% less landfill waste in craft projects |
| Short-lived structures (20-30 year lifespan) | Time-tested joinery techniques | Buildings enduring 100+ years |
| Worker disconnection from projects | Ownership of entire process | Higher job satisfaction and quality control |
Developing Building Craft Skills: A Practical Framework
True building craft isn't learned through videos alone—it requires deliberate practice. Here's how to progress from beginner to skilled practitioner:
- Master Foundational Movements
- Spend 100+ hours practicing hand-planing to feel wood grain resistance
- Learn to cut perfect mortise-and-tenon joints without power tools
- Develop Material Literacy
- Identify wood species by smell, weight, and fracture patterns
- Understand how humidity affects different materials seasonally
- Implement Craft Feedback Loops
- Document every project failure in a physical journal
- Seek critiques from builders with 20+ years experience
The Sustainable Advantage of Building Craft
While "green building" often means adding expensive tech, building craft achieves sustainability through inherent practices:
Craft-Driven Sustainability Principles
- Waste = Resource: Sawdust becomes particleboard; offcuts become joinery
- Longevity = Sustainability: A well-crafted door lasts 5x longer than factory-made
- Local Sourcing = Lower Impact: Using regional materials reduces transport emissions
Consider timber framing—a building craft technique where joints are cut to exact tolerances. Unlike steel-framed structures requiring specialized demolition, these buildings can be disassembled and materials reused centuries later. This isn't just eco-friendly; it's future-proof construction.
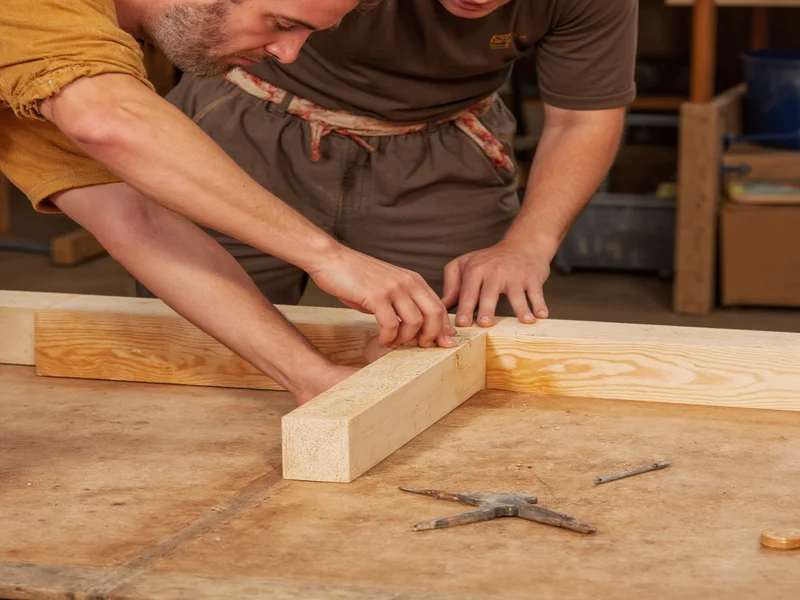

Overcoming Modern Barriers to Building Craft
Time constraints and cost pressures threaten craftsmanship, but these strategies preserve quality:
- The 10% Rule: Dedicate 10% of project time to hand-finishing details machines can't replicate
- Client Education: Show comparative samples of rushed vs. crafted work early in projects
- Micro-Specialization: Master one technique deeply (e.g., perfecting window sills) before expanding
Remember: Building craft isn't about rejecting modern tools—it's about using technology to enhance, not replace, human judgment. A laser level ensures accuracy, but only the craftsman's eye determines if a joint feels "right" under pressure.











 浙公网安备
33010002000092号
浙公网安备
33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4